Statement of Financial Position Overview:
A statement of financial position (formerly called a balance sheet) is a financial report about the financial position of an entity. It is a snapshot of the company’s financial condition at a specific moment in time (usually the month-end or year-end).
The statement of financial position is a detailed representation of the accounting equation. Let’s understand this equation.
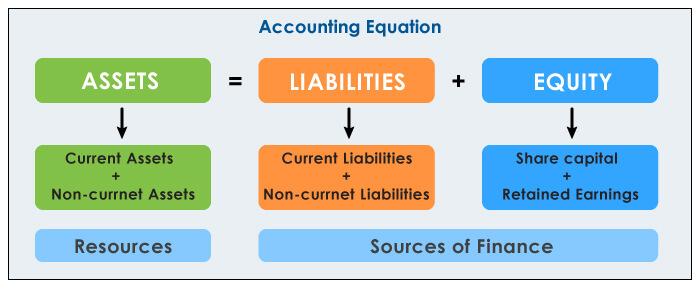
This equation is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. It ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced. It also explains that all the resources (Assets) that an entity owns are financed through debt (liabilities) and equity (capital).
A statement of financial position is a historical report. It shows the actual position of accounts present on the day of the report. It is prepared at the end of the month, quarter, year, however, we can prepare at any particular date to show the financial position of the entity.
Components of the statement of financial position
The statement of financial position has three key components: Assets, liabilities, and equity.
Assets
Assets are valuable economic resources that a business entity owns for future economic benefits.
There are two types of assets based on physical existence. Tangibles (physical existence) and intangibles (non-physical existence).
We can further categorize assets into current and non-current assets. Current assets are those that are easily convertible into cash within a year, while non-current assets are not convertible into cash before a year.
A few examples of assets are cash, accounts receivable, office supplies, inventory, land or building, furniture, and goodwill.
Liabilities
Liability is a present obligation of an entity. It arises out of past transactions or events.
For instance, an account payable arises out of the past purchase of goods or services.
We classify it into current and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are obligations due within one year while long-term liabilities are those that are due after one year.
A few examples of liabilities are accounts payable, wages payable, income tax payable, short-term loans, deferred tax liabilities, and long-term debts.
Equity
Equity (also called owner’s equity or shareholder’s equity) is the actual value of funds that owners of the entity invest in the business. It is the value after we deduct the liabilities from the value of assets.
We can classify the equity of the company into share capital, retained earnings, and other reserves.
Format of the statement of financial position
The format of statement of financial position is often presented differently under IFRS and GAAP.
Companies that follow IFRS, present statement of financial information under this order:
- Non-current assets
- Current assets
- Equity
- Non-current liabilities
- Current liabilities
Under IFRS, companies list the current assets in the reverse order of liquidity.
While companies that follow GAAP, present the statement of financial position information in the order of liquidity:
- Current assets
- Non-current assets
- Current liabilities
- Non-current liabilities
- Equity
There is no specific format for a statement of financial position that must be used. However, there are two general formats: account format and report format.
Account format is of two columns displaying assets on the left column and liabilities and equity on the right column while the report format (often called traditional format) has only one column.
We have presented the formats below following the GAAP.
1-Account Format (As per GAAP)

2-Report Format (As per GAAP)
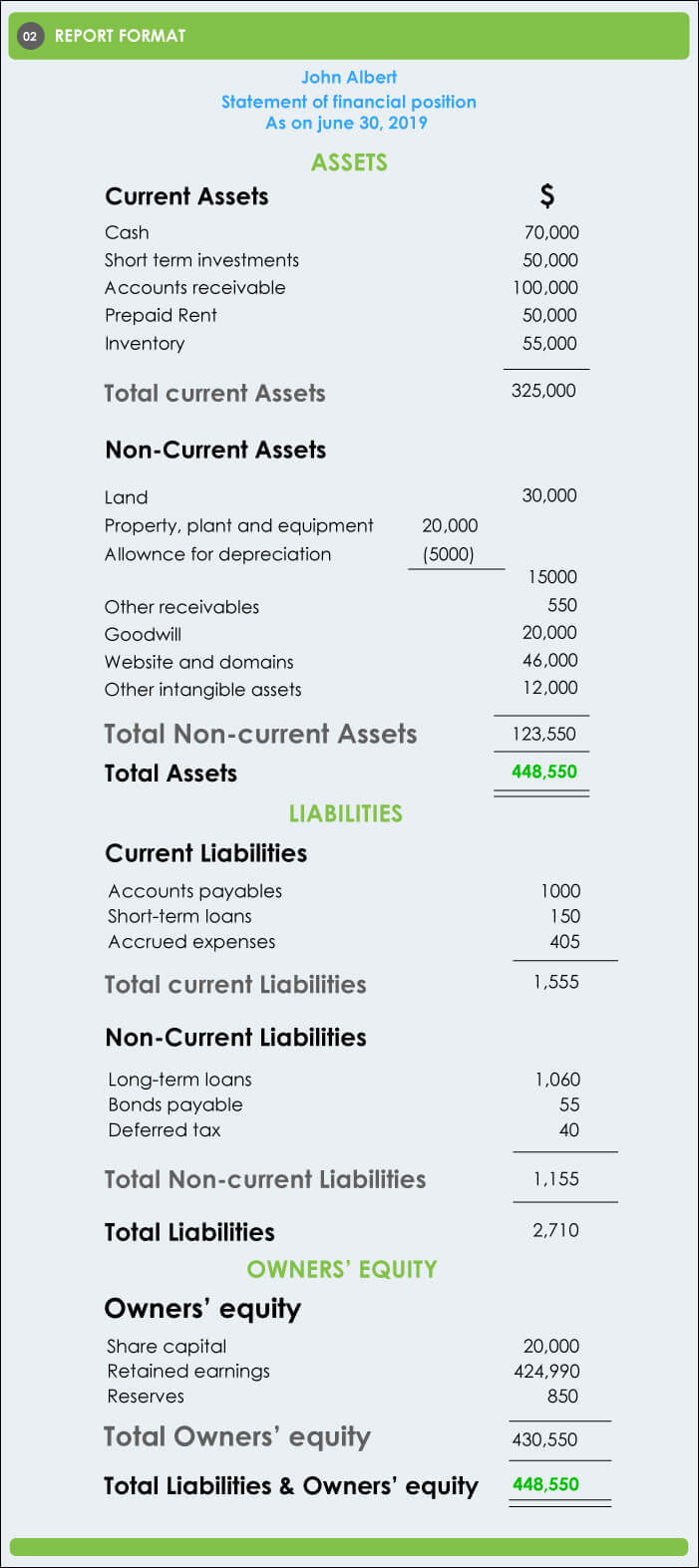
Which one is the better format? Well, it depends on the preference of the reader who reviews the document.
Report format is comparatively easier to read and fits well on the standard size of the paper, however, there is no restriction under IFRS or GAAP to use a specific format.
Importance
As per IAS 1, the statement of financial position is an important part of a complete set of the Financial Statements of an entity.
It is a financial document that keeps up-to-date to the owners and other stakeholders about the company’s financial standing.
Statement of financial position is particularly important to:
- Know the net worth of the business
- Determine the working capital of the business
- See if the entity Can sustain future operations
- Defend from tax proceedings
- Identify the rate of dividend
- Know if your business qualifies for bank loans
We can evaluate and track the financial metrics of the business entity with this document. It is an instrument that accountants or financial analysts use to make decision making for the business entity.


